|
Six-year program (enrollments after the 102nd academic year)
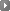 The clinical and basic medicine curriculum design of the Department of Medicine, MacKay Medical College, is based on core clinical problems and used systemic integrated basic and clinical courses. Since the 102nd Academic Year, the students must obtain 241.3 credits for graduation in the six-year based curriculum. It is primarily divided into the following three stages: The clinical and basic medicine curriculum design of the Department of Medicine, MacKay Medical College, is based on core clinical problems and used systemic integrated basic and clinical courses. Since the 102nd Academic Year, the students must obtain 241.3 credits for graduation in the six-year based curriculum. It is primarily divided into the following three stages:
 First and second year: General education and basic education of the Department of Medicine First and second year: General education and basic education of the Department of Medicine
Students are guided to develop positive life values with the spirits of MacKay so that they will eventually become social intellects with medical responsibilities. Meanwhile, students are cultivated to develop self-discovery and problem-solving abilities. Their language proficiency is enhanced, establishing the basis of the individual and professional training.
The general education courses are divided into four main strata: Tien (天) pertaining to“heaven”, Di (地) pertaining to“science”, Ren (人) pertaining to“humanities,” and Xing (心) pertaining to“arts.” All undergraduates are requested to complete at least 28 credits in above strata. The curriculum includes MacKay Lectures, Chinese, English, Science of religion, Humanities, Arts, Foreign language and Local language. Detail information on the courses of general education please contact to the following website: https://www.mmc.edu.tw/Holistic-eng/Curriculum.asp
Except the general education, basic science courses are integrated and connected throughout the first and the second year, including Calculus, General Physics, General Chemistry with Laboratory, Organic Chemistry with Laboratory, Biochemistry with Laboratory and General Biology with Laboratory, Introduction to Digital Medicine, Biostatistics, Medical Humanistic Courses. Moreover, medical core course such as Human Structure with Laboratory, medical protozoology and Virology are also provided.
 Third and fourth year: Integrated basic medical education Third and fourth year: Integrated basic medical education
The third-year curriculum is the integration of contents based on the general structure, functions, pathology and behaviors of a normal person.
The third year is mainly consisting of the different subjects of clinical basic medicine, including the following four major parts:
1. Human body structure: Practice Anatomy with Laboratory, and Neuroanatomy with Laboratory.
2. Human functions: Physiology with Laboratory.
3. Pathogenesis: Pathology with Laboratory.
4. Pathogens and defense systems: Immunology/Microbiology with Laboratory, and Pharmacology with Laboratory.
All of above subjects are divided into multiple modules by organ system, including Introduction to Human physiology and pathology、Host defense (I):Immunology and Parasitology、Cardiovascular System、Musculoskeletal and Pulmonary Systems、Host defense (II):Bacteriology、Urinary, Reproduction and Endocrine Systems、Digestive System、Brain and Behaviors。Modules cooperate with PBL lesson plans for integrated courses every semester. In addition, independent teaching courses are also implanted, including Hospital and Community Volunteer Services and Life and Death Education.
The fourth-year curriculum is the integration of contents based on the concise ciinically relevant anatomical structure, functions, and behaviors of abnormal and diseased persons, as well as clinical knowledge and skills.
It includes the different clinical disciplines, clinical diagnostics, experimental diagnostics, imaging diagnostic medicine, and others.
The above subjects are divided into multiple modules based on the organ systems, including Introduction to Clinical Medicine, Cardiovascular System、Pulmonary System, Endocrine and Metabolism、Gastrointestinal System、Brain and Behaviors、Musculoskeletal System and Integument System、Host Defense and Infection、Fluid, Electrolytes, Renal and Genitourinary System、Hematology and Oncology.
In systemic modules, PBL are implanted and integrated into semesters. Also, independent teaching courses are provided in the curriculum, including Clinical Diagnosis Medicine Practice、Community Medicine (I)(II)、Community Medicine and Practice(I)(II)、Problem-Based Learning、Introduction to Oral Medicine、Forensic Medicine、Communication Skills in Healthcare、Laboratory Diagnosis Practice、Introduction to Translational Medicine、Medical Chart Writing(I).
 Fifth and sixth year: Clinical medicine education Fifth and sixth year: Clinical medicine education
Based on the teaching methods of simulation training, field observation, mission-oriented learning, and evaluation-based education, students are educated to become doctors with the basic core competencies.
The fifth-year clinical medicine education includes Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pediatrics, Medical Chart Writing, Evidence-Based Health Care, Clinical Skill Training, Ophthalmology, Otolaryngology, Anesthesiology, and Medical Ethics and Law. Intern training includes Core Clerkship - Internal Medicine (12 weeks), Core Clerkship-Surgery (12 weeks), Core Clerkship-Pediatrics (5 weeks), Core Clerkship-Obstetrics/Gynecology (5 weeks), and Clerkship-Community & Family Medicine (2 weeks).
The sixth-year Clinical training includes Core Practical Training (Internal Medicine) (II)(6 weeks), Core Practical Training (Surgery) (II)(6 weeks), Clerkship-Ophthalmology(2 weeks), Clerkship-ENT (Ear, Nose and Throat)(2 weeks), Clerkship-Dermatology and Allergy Immunology/ Rheumatology(2 weeks), Clerkship-Emergency Medicine(2 weeks), Clerkship- Rehabilitation Medicine(2 weeks), Clerkship-Anesthesiology(2 weeks), Clerkship-Radiology(2 weeks), Medical Services to Remote Areas(2 weeks), Clerkship-Neurology(4 weeks), Clerkship-Radiation Oncology & Hematology Oncology(4 weeks), Clerkship-Psychiatry & Hospice Palliative Care(4 weeks), and Clerkship-in/outside the School(8 weeks).
|